Banks to start race to raise new capital in early 2024?

[ad_1]
 ©Reuters
©Reuters According to Donghai
Investing.com – In early 2024, after the State Bank (SBV) issued official approval documents approving the capital increases of many banks, many joint-stock commercial banks announced capital increase plans. The charter approves a variety of options, such as issuing shares to pay dividends, private placements, issuing shares to foreign strategic investors… Correspondingly, banks allowed to increase their registered capital include: Lien Viet Post Commercial Joint Stock Bank (HM:) (LPBank), National Commercial Joint Stock Bank (NCB), Saigon Industrial and Commercial Joint Stock Bank (SaigonBank)…
On January 2, NCB said it had just received approval from the National Bank to increase its authorized capital to more than 11.8 trillion VND. Accordingly, NCB will issue and sell 620 million shares at a price of VND10,000 per share to increase its registered capital by VND6.2 trillion. If the issuance is successful, NCB’s registered capital will increase from VND 5,602 billion to VND 11,802 billion. According to the plan, NCB will issue shares as soon as it obtains approval from the State Securities Regulatory Commission (expected in the second quarter of 2024). The transfer period of these shares is within one year from the date of completion of this issuance.
LPBank has just received approval from the National Bank to increase its registered capital from VND20,576 billion to more than VND25,576 billion. Previously, LPBank was also approved to increase its registered capital by up to VND 11,385 billion based on the plan approved at the 2023 Annual Shareholders Meeting. Specifically, the bank issued more than 328.5 million shares, paid dividends at a 19% dividend rate, and issued additional shares worth the equivalent of VND5 trillion to existing shareholders. After increasing its registered capital, LPBank continues to rank among the private joint-stock commercial banks with the largest registered capital in the system.
At the end of December 2023, Saigon Bank was also approved to increase its maximum authorized capital by VND308 billion in the form of stock issuance to pay dividends to existing shareholders. Bank representatives said that increasing registered capital is necessary for Saigon Bank to improve its financial capabilities and innovate technology to keep up with development trends.
Previously in 2023, the National Bank also issued a document approving 21 joint-stock commercial banks to increase their charter capital, mainly from the bank’s equity capital (undistributed profits and reserves). Approved banks include: HDBank (HM:), MB, SeABank, ACB (HM:), VIB (HM:), TPBank, LPBank, BacABank, VietABank, VietBank, Techcombank (HM:), Eximbank (HM:), OCB , AB Bank, SHB (HM:), BVBank, MSB, KienLongBank, NAMABank, NCB, VPBank (HM:).
For state-owned commercial banks, SBV also submitted to the Prime Minister to consider adding state capital to BIDV (HM:) from residual profits after tax to establish a fund in 2021 and instructed Vietcombank (HM:) to complete plans to establish a fund in 2021 After that, capital is added from the residual profit after tax…
Registered capital is a key component in calculating the capital adequacy ratio (CAR) and ranking credit institutions. The CAR coefficient is calculated in accordance with Document No. 41, which is close to the international standard of the New Basel Agreement, and the minimum setting is 8%.
According to the “2021-2025 Credit Institutions Bad Debt Processing System Reorganization Plan”, the banking industry strives to have the capital adequacy ratio of commercial banks no less than 10-11% by 2023, and by 2025, it will reach at least 11-12%.
However, experts said that although banks continue to have capital increase plans, especially in the fourth quarter of 2023, a series of banks have stepped up the implementation of the final procedures to distribute stock dividends to shareholders as planned, thus having more resources to increase registration capital, but Vietnam’s banking system is still capital-starved and its CAR coefficient is much lower than in other parts of the world. In particular, many countries in the region have applied Basel III or parts of Basel III.
According to the latest data released by the National Bank, as of May 2023, the total statutory capital of the entire credit institution system reached 888,864 billion VND, an increase of 1.35% from the end of 2022.
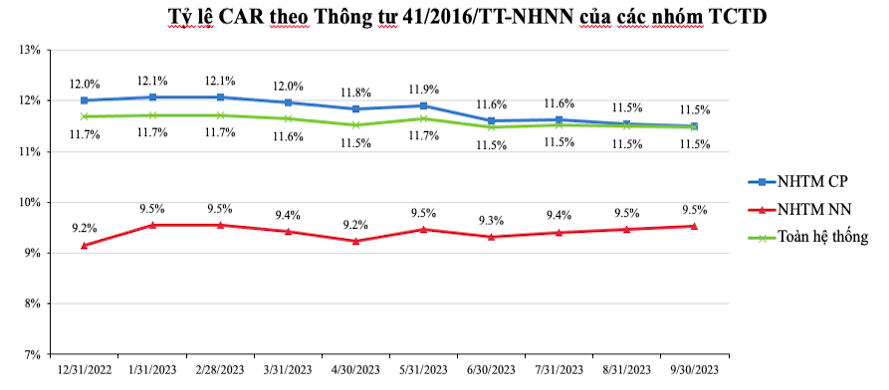
The capital adequacy ratio of credit institutions and foreign bank branches applied for under Document No. 41/2016/TT-NHNN reached 11.70% (a slight decrease from 11.68% at the end of 2022), among which the capital adequacy ratio of state-owned commercial banks accounted for 9.53% of bank groups. % (up 0.37 percentage points from the end of 2022); joint-stock commercial banks reached 11.90% (down 0.11%); foreign bank groups accounted for 21.21% (up 2.05 percentage points).
PhD. Economic expert Nguyen Tri Hieu said the private commercial banking industry continues to target higher capital adequacy ratios than before due to initiatives in capital management and building capital closer to Basel III standards. Loan growth.
The general manager of a commercial bank said that large registered capital allows the bank to increase the scale of assets, improve financial capabilities, and further expand credit for business activities by increasing the grant limit. Therefore, it is extremely necessary for banks to increase capital and improve financial capabilities in 2024.
Fitch Ratings also believes that Vietnam’s credit growth has been quite rapid in recent years, requiring banks to increase capital and ensure safety ratios: “The banking system needs to increase capital by up to 10% of USD 7 billion (2.9% of GDP) to insure risks and maintain CAR The coefficient is 10%.”
Analysts predict that in 2024, the banking industry will still face difficulties such as bad debts and a continued increase in potential risky debt. In addition, banks also play the role of financial backbone to support enterprises in resuming production and operations. Therefore, high registered capital will become a “buffer” to help commercial banks have more resources to cope with difficulties and challenges, especially in the current turbulent economic environment, where the pressure to increase capital is weighing heavily on banks. This capital increase also creates the foundation and conditions for commercial banks to continue to support enterprises and the economy in resuming production and operating activities.




